The Dayak people are the native inhabitants of Kalimantan, the Indonesian part of Borneo Island. They belong to the Austronesian group, whose ancestors migrated from Taiwan roughly two thousand years ago.
These early settlers travelled south through the Philippines before reaching Borneo, where they adapted to the island’s dense forests and river systems.
Physically, Dayak people share some features with the wider Mongoloid group, though they are not Chinese. Many Dayak men carry the Y-DNA haplogroup O, a genetic marker common among Austronesian peoples.
Who Are the Dayak People?
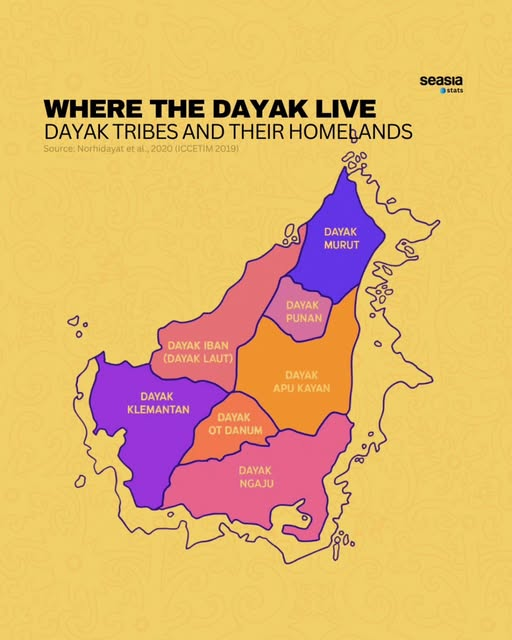
Map of Dayak communities across Borneo Island.
The name Dayak (also written Dyak, Dayuh, or Dajak) is a collective term for over 200 different ethnic groups living mainly in the interior and riverine regions of Borneo. Each group has its own language, customs, and traditions, yet they share many features that identify them as Dayak.
Their languages belong to the Austronesian family, linking them to other peoples across maritime Southeast Asia.
Traditionally, the Dayaks followed Kaharingan, an animist belief system based on respect for nature and ancestral spirits. From the 19th century onward, many converted to Christianity or Islam due to missionary influence and colonial contact.
Today, several million Dayaks live in both Indonesia (Kalimantan) and Malaysia (Sarawak and Sabah).
Major Dayak Ethnic Divisions
The Dayak peoples are divided into several major groups, each with distinct dialects and customs. The main divisions include:
Ngaju:
Apo Kayan/Orang Ulu:
Iban:
Bidayuh:
Kadazan, Dusun, Murut:
Punan:
Ot Danum:
These groups are often identified by their location. Whether they live in the river valleys, mountain regions, or forest interiors and by their distinct cultural expressions such as weaving, woodcarving, and traditional tattooing.
Changing Way of Life
Traditional Dayak attire featuring detailed beadwork and handwoven fabrics.
In earlier times, Dayak communities lived in large wooden longhouses shared by many families. Their livelihoods depended on farming, hunting, and fishing.
Today, many Dayaks live in urban centres and have adopted modern ways of life. Clothing, education, and occupations have changed, yet their traditional art, music, and festivals remain central to their identity.
Festivals such as Gawai Dayak in Malaysia and Naik Dango in Indonesia continue to celebrate their shared heritage and community spirit.
Cultural Legacy
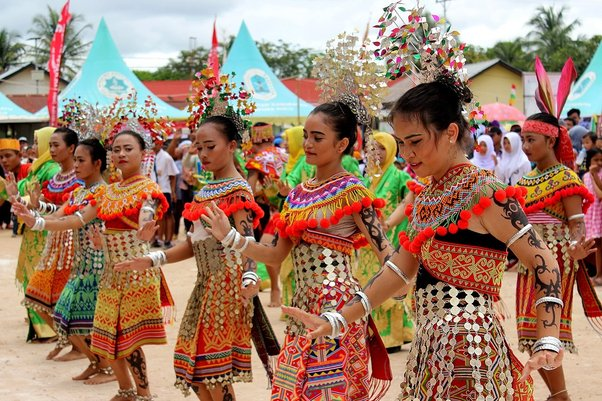

Dayak dancers performing at a cultural festival.
The Dayak people have preserved their traditions through generations despite rapid social and economic change. Their deep respect for the environment, art, and community remains a defining part of Borneo’s cultural identity.
The story of the Dayak is not only one of the past but also of resilience and continuity in the modern world.
Dayak Music
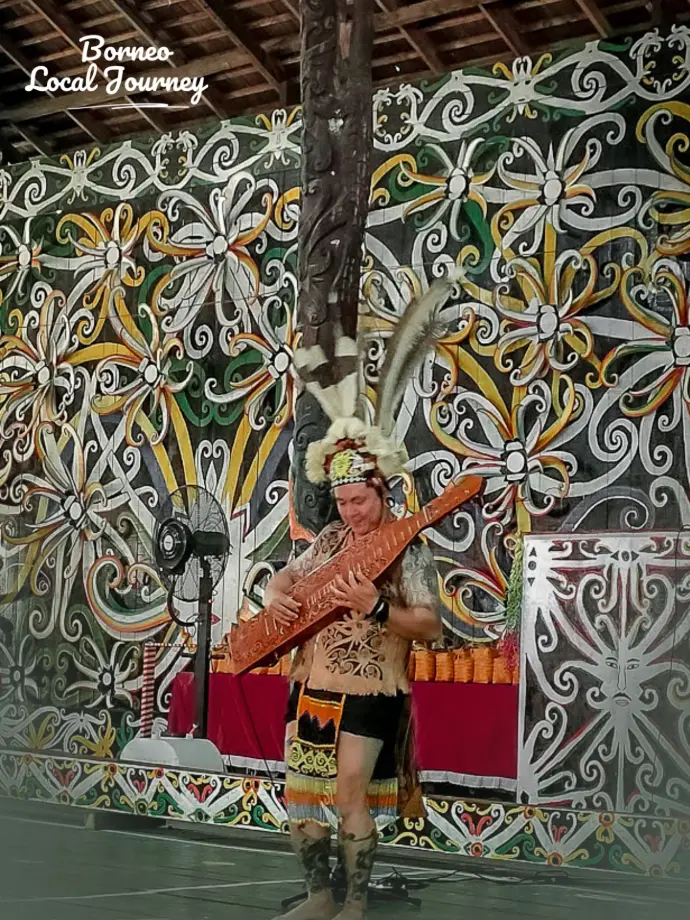

Dayak musicians performing traditional songs during a community festival.
Music holds an important place in Dayak culture. It is not only a form of entertainment but also a means of passing on stories, beliefs, and history. Traditional Dayak music reflects the rhythms of daily life, the sounds of the forest, and the spiritual connection between people and nature.
The most common instruments are gongs, drums, and stringed instruments made from bamboo or wood. The sape’, a carved wooden lute from the Orang Ulu people, is the best-known Dayak instrument. It produces soft, flowing melodies often played during ceremonies, dances, and gatherings.
Songs are usually performed in groups and accompanied by dance. The lyrics often tell stories about ancestors, bravery, and harmony with the natural world. Each community has its own musical style, and performances differ from one region to another.
In modern times, Dayak music has blended with contemporary forms. Musicians now use guitars and keyboards alongside traditional instruments. This mix helps keep Dayak music alive while introducing it to younger generations and wider audiences.
Your Journey Awaits

A Day with Dayak heritage and daily life.
Visiting Borneo offers more than a holiday. It is a chance to experience a living culture shaped by nature and tradition. Meeting Dayak communities, hearing their stories, and seeing their craftsmanship first-hand gives real insight into the island’s deep roots.
For those who wish to explore respectfully and with care, Borneo Local Journey helps travellers connect with the island and its people in a thoughtful way. Each trip is planned around personal interests, from cultural visits to rainforest adventures. Local guides share their knowledge and make sure each experience supports the communities involved.
Travel with confidence knowing that everything, transport, accommodation, and guidance is arranged by professionals who understand the land and its traditions.
If you would like to plan your own journey, you can reach us at:
📞 +6285172034410 (Call / WhatsApp)
✉️ alma@borneolocaljourney.com
Or Fill the Form
One of your Borneo specialist will contact you soonest.